Overview
Guide walking set by step through preparing Azure Devops self hosted agent running in AKS and intial Azure Devops setup.
Configuring Azure Devops self hosted agent
Prepare Dockerfile
- create a Dockerfile for deploying the self hosted agent referencing the template from the Microsoft documentation.
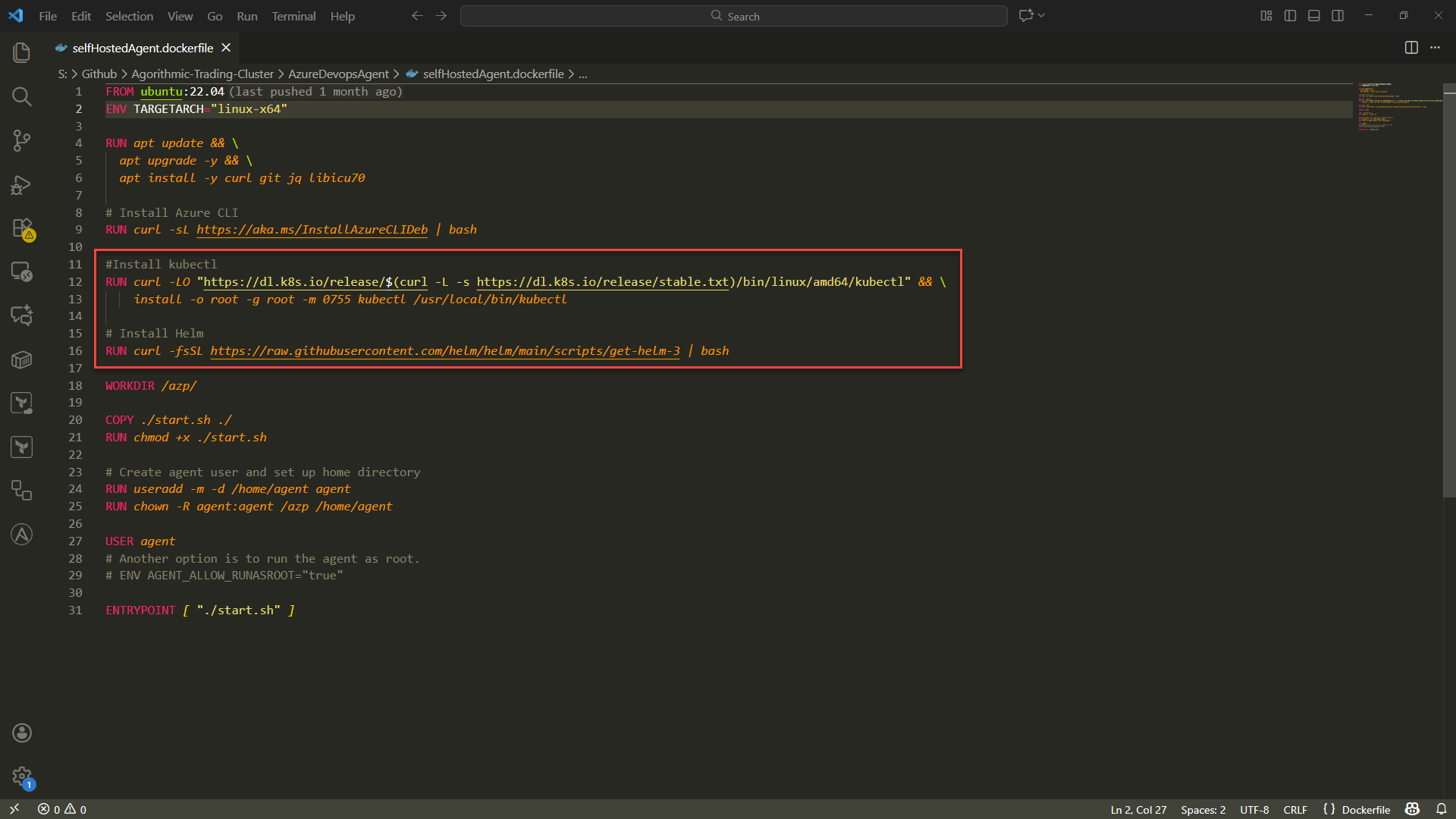
- Add kubectl and helm to the Dockerfile. The pipeline will use these within the pipeline to execute comands within the cluster.
#Install kubectl
RUN curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl" && \
install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
# Install Helm
RUN curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3 | bashaz acr build --registry <acr-name> --image <image-name>:<version> --file selfHostedAgent.Dockerfile .Creating Azure Devops Personal Access Token
A Personal Access Token is used in place of credentials to authenticate to Azure Devops for granting access to self hosted agents another function such as integrating external tools into pipelines.
- Before crating the PAT, create a new Azure Devops project if one does not already exist for this project.
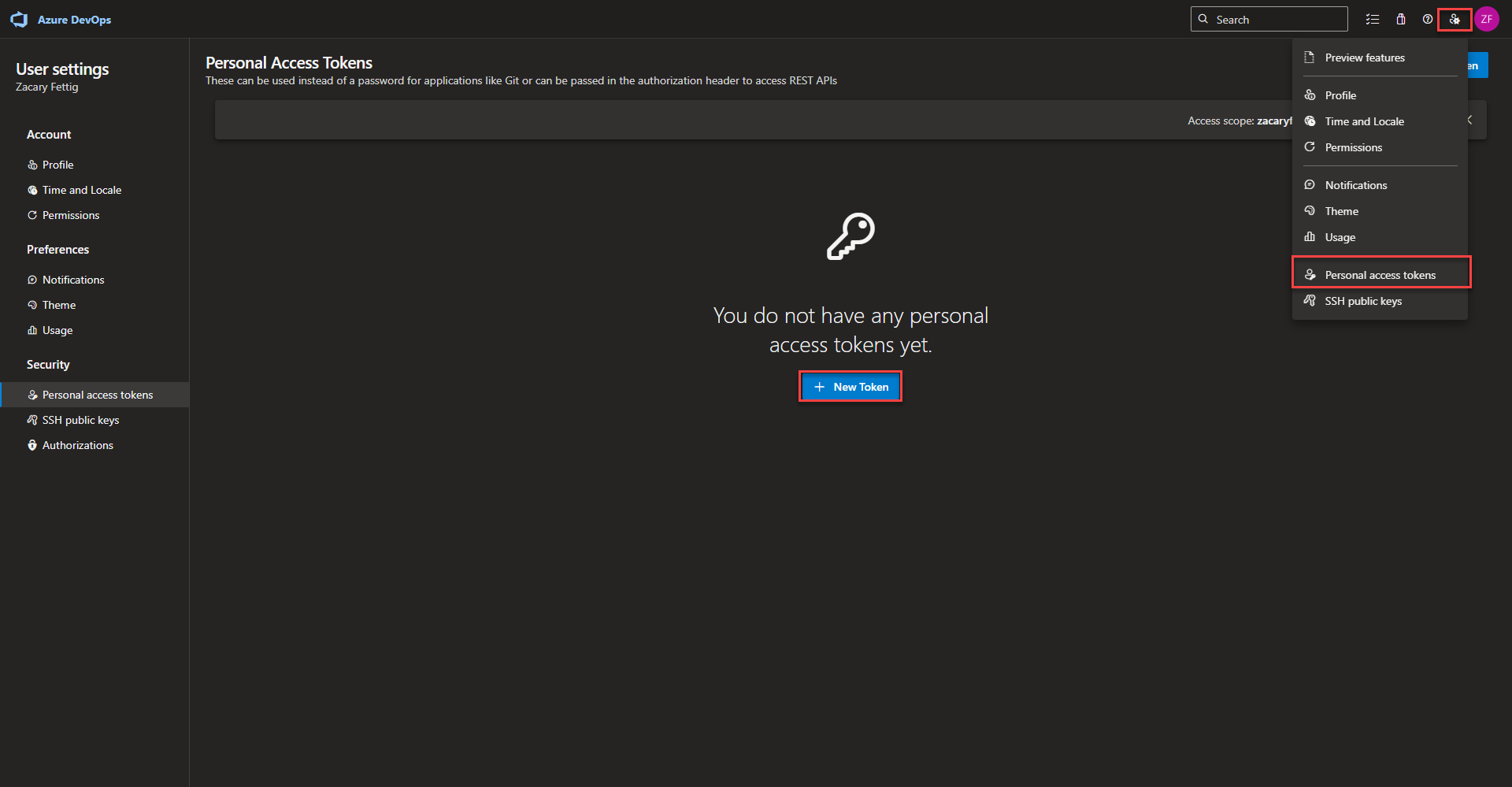
- Create new token by navigating to the person icon in the upper right and selecting Personal access token. Click the + New Token button. Enter a name for the token. Expiration day length. Set scope to custom defined. Make sure Agent Pools read and manage are selected. Select create.
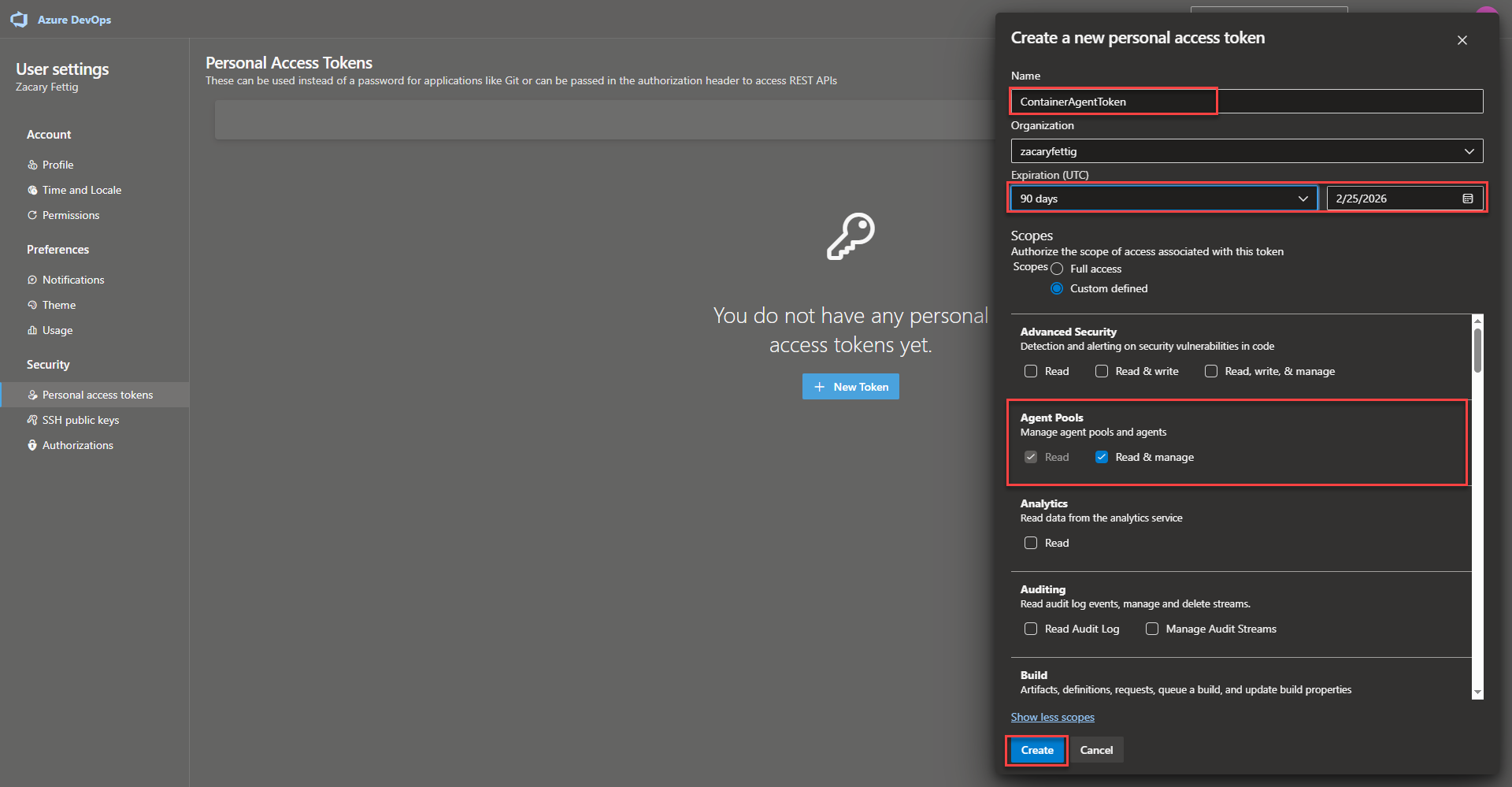
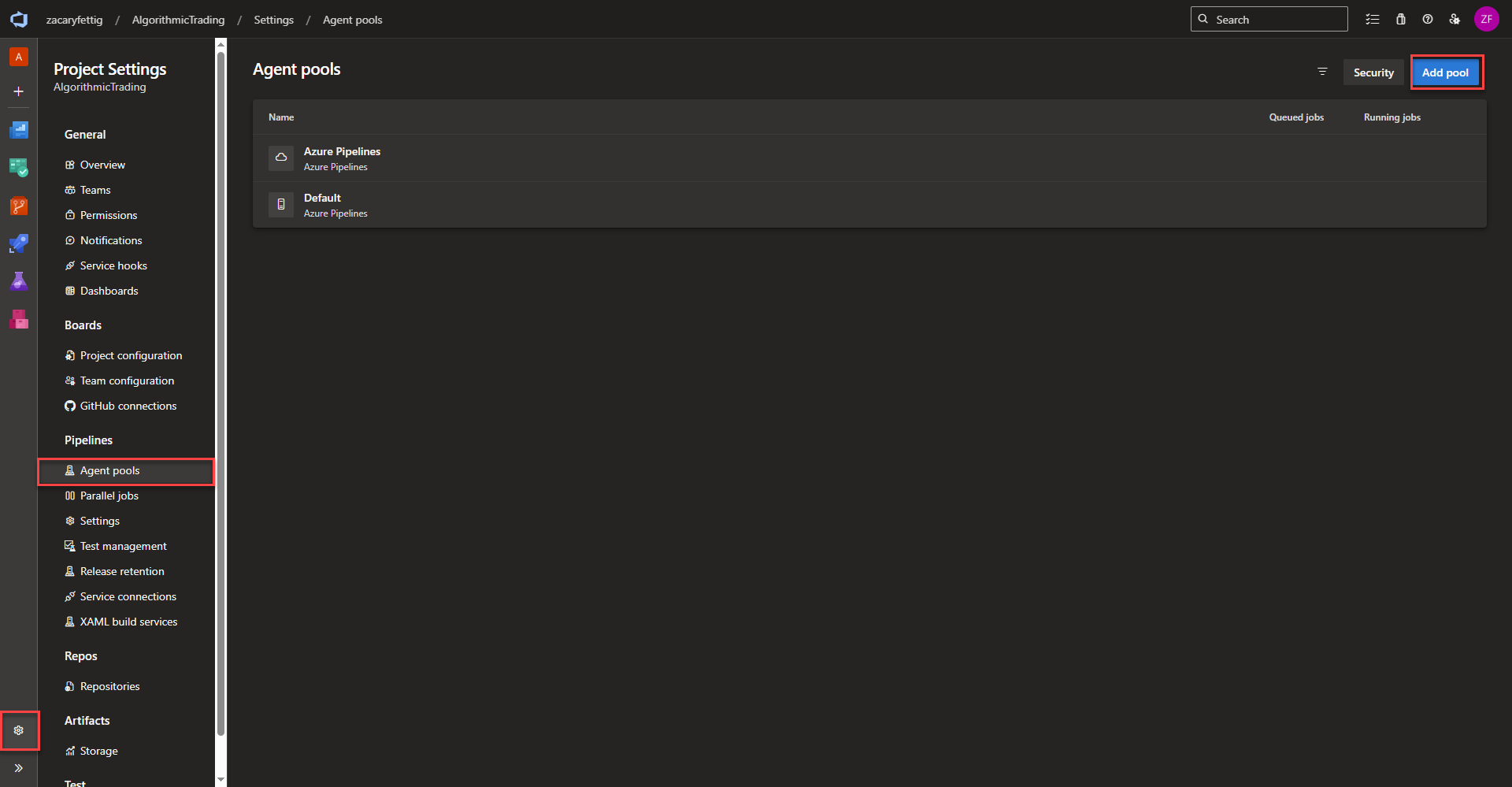
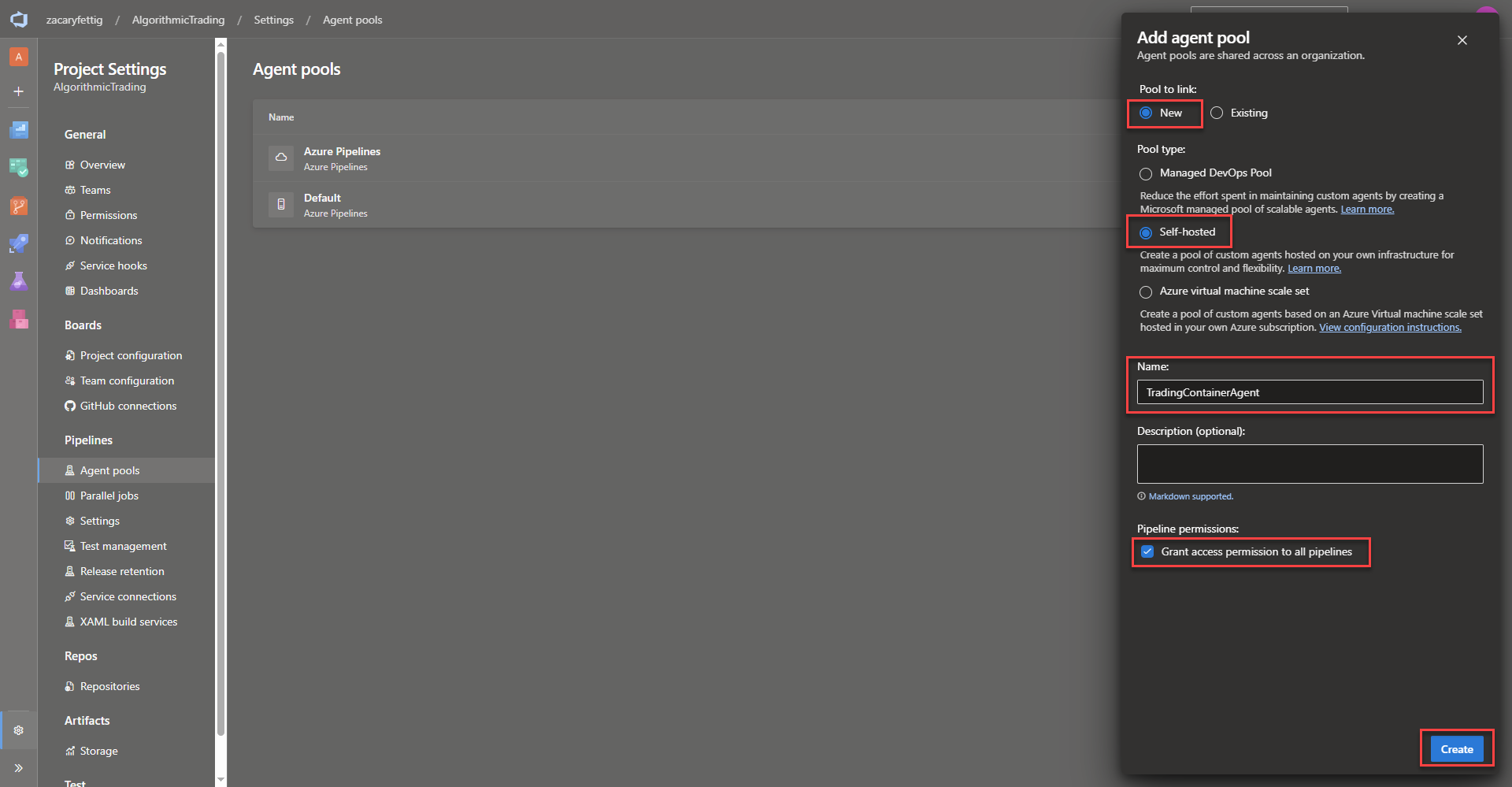
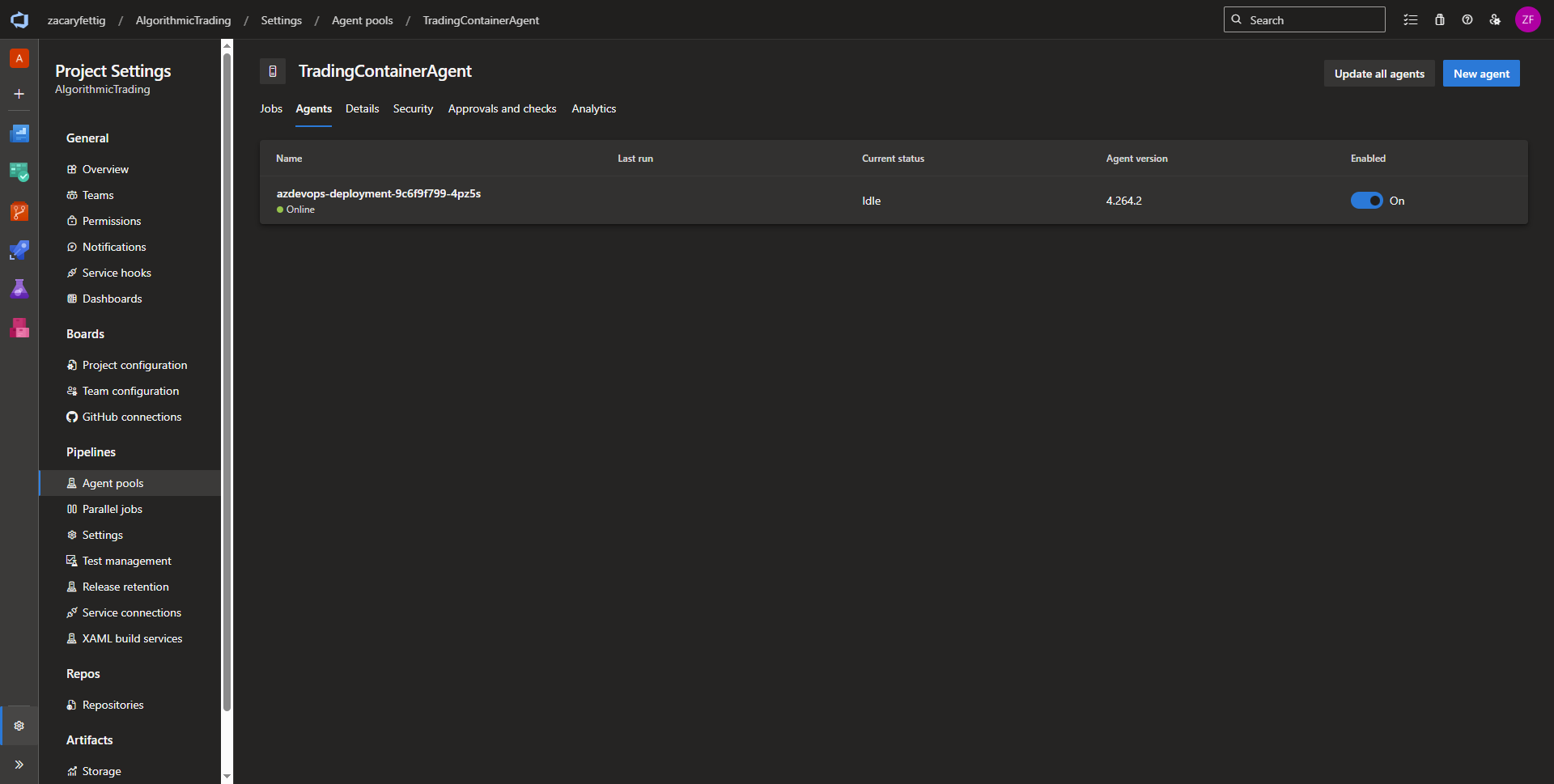
Creating an Azure Devops Agent Pool
An agent pool is a grouping of agents that manages job scheduling and controls which pipelines can use which agents. Microsoft hosted agents are managed by Microsoft that don’t require any manual infrastructure setup, but doesn’t have access to private networks and extra costs for parallel jobs. Self hosted agents can easily connect to private networks add cost savings. This project deploys a self hosted agent that is hosted within Kubernetes allowing pipeline deployment within the cluster and connected vnets.
Overview of the AKS Self Hosted Agent deployment YAML
The yaml defines a Kubernetes Deployment that pulls the ACR Self Hosted Agent Image and runs it within the cluster. It creates a Pod/Pods in the devops-agent namespace, pulls the image from Azure Container Registry, starts the Azure DevOps agent processes inside the container, and keeps the agent running continuously. A Kubernetes Deployment ensures consistent configuration across restarts, automatic Pod restarts, and flexible scaling.
Sections within the code:
- Kind: Tells the cluster that its creating a Deployment resource using the apps/v1 API
- Metadata: Gives a name to the deployment and determines which namespace it should be deployed into.
- Labels: Labels are how Kubernetes resources link together. The Deployment uses the selector to identify the pods it manages.
- Replicas: Tells Kubernetes how many pods to run. Kubernetes will automatically create a replacement if a pod fails.
- Template: The section below template, including the containers section, defines what a pod should look like.
- Containers: Specifies the image and pulls from ACR at run time.
- Env: Replaces the variables from the Kubernetes Secret that will be created later on when deploying the yaml to the cluster. The name is the name of the Kubernetes Secret and the key is the variable that is specified in the secret.
- VolumeMounts: mountPath: /var/run/docker.sock allows the container to issue Docker API calls and control the host’s Docker engine. Mounts the HostPath volume.
- HostPath: path: /var/run/docker.sock allows the container to build images, run containers, mount host filesystems. Enabling a Docker within Docker scenario.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: azdevops-deployment
namespace: devops-agent
labels:
app: azdevops-agent
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: azdevops-agent
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: azdevops-agent
spec:
containers:
- name: kubepodcreation
image: kubetrading.azurecr.io/selfhostedagent:latest
env:
- name: AZP_URL
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: azdevops
key: AZP_URL
- name: AZP_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: azdevops
key: AZP_TOKEN
- name: AZP_POOL
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: azdevops
key: AZP_POOL
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /var/run/docker.sock
name: docker-volume
volumes:
- name: docker-volume
hostPath:
path: /var/run/docker.sockDeploy Devops Self Hosted Agent to Kubernetes
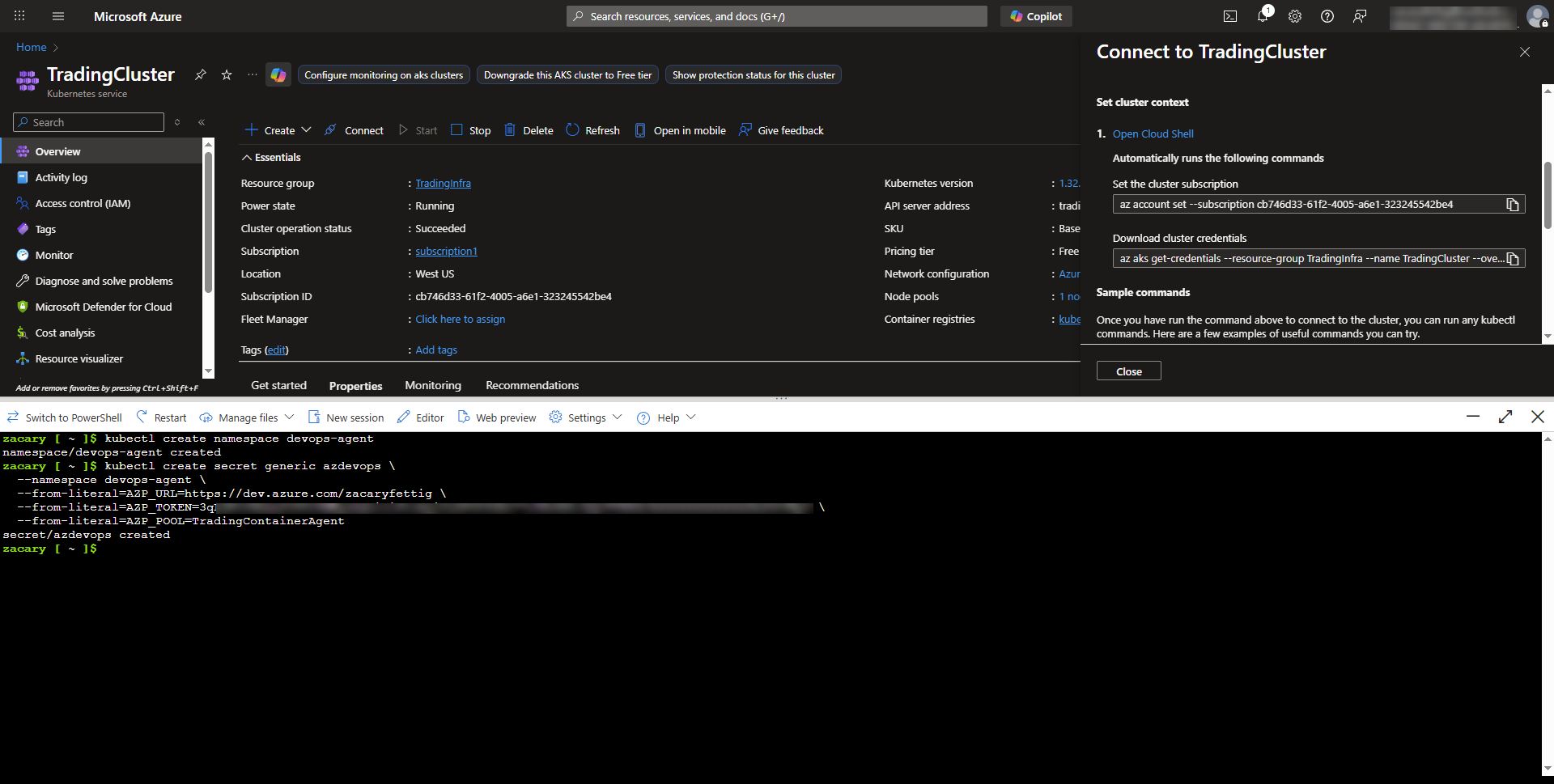
- First deploy the Kubernetes secret that specifies the namespace that the devops agent will be deployed in, the Token information, and the Azure Devops Pool.
- AZP_URL: Is the url of the Azure DevOps organization
- AZP_TOKEN: Specifying the Personal Access Token
- AZP_POOL: The name of the pool created earlier
Create namespace and deploy secrets
kubectl create secret generic azdevops \
--namespace devops-agent \
--from-literal=AZP_URL=https://dev.azure.com/zacaryfettig \
--from-literal=AZP_TOKEN=3qLdPtO6bma2IUOI6MWgzmQnioi6towgjCuGP0f3GXv77rTBvRXtJQQJ99BKACAAAAAAAAAAAAASAZDO3NpC \
--from-literal=AZP_POOL=TradingContainerAgent3. Apply Kubernetes yaml deployment.
kubectl apply -f azDevopsAgent.yaml